Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have developed a new method for 3D printing gels and other soft materials. The research was published in a new paper, and it has the potential to create complex structures with nanometer precision.
Because many gels are compatible with living cells, this new method can quickly start producing soft micro-medical devices, such as drug delivery systems or flexible electrodes that can be inserted into the human body.
Standard 3D printers work by creating thin sheets of material (usually plastic or rubber) and constructing them layer by layer (such as lasagna) until the entire object is made.
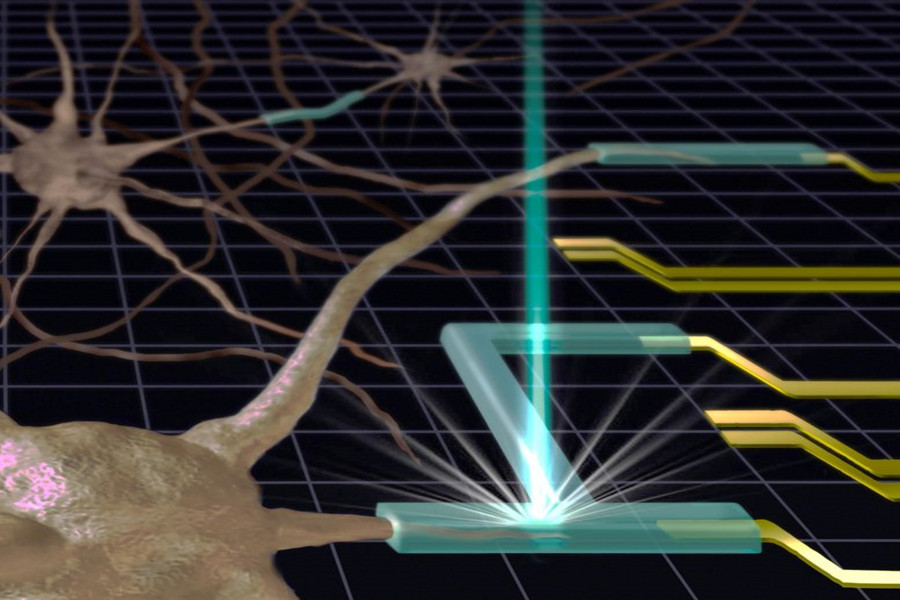
NIST researcher Andrei Kolmakov said that using a 3D printer to make objects made of gel is “a bit like a delicate cooking process.” In the standard method, the 3D printer chamber is filled with long-chain polymer soup (long-chain molecules held together) dissolved in water. Then add “fragrance” (a special molecule that is sensitive to light). When the light from the 3D printer activates these special molecules, they stitch together polymer chains to form a fluffy network structure. This kind of gel is still surrounded by liquid water.
Generally, modern 3D gel printers use ultraviolet or visible lasers to promote the formation of gel scaffolds. However, Kolmakov and his colleagues focused their attention on another 3D printing technology that uses electron beams or X-rays to make gels. Because these types of radiation have higher energy or shorter wavelengths than ultraviolet and visible light, these beams can be more tightly focused, so gels with finer structural details can be produced. These details are exactly what tissue engineering and many other medical and biological applications require. Electrons and X-rays also have a second advantage: they do not require special molecules to promote gel formation.
But currently, such tightly focused sources of short-wavelength radiation (scanning electron microscopes and X-ray microscopes) can only operate in a vacuum. There is a problem because in the vacuum the liquid in each chamber evaporates instead of forming a gel.
Kolmakov and his colleagues at NIST and Trieste, Italy solved this problem and demonstrated the use of 3D gel printing technology in the liquid by placing an ultra-thin barrier (a layer of silicon nitride thin film) between the vacuum and the liquid chamber. The flakes prevent the liquid from evaporating (which usually occurs in a vacuum), but allow X-rays and electrons to penetrate into the liquid. This method allowed the team to use 3D printing methods to create gels with structures as small as 100 nanometers (nm) (1000 times thinner than human hair). By improving their method, the researchers hope to imprint a 50-nanometer structure on the gel.
Some structures made in this way may be used in the future for flexible injectable electrodes for monitoring brain activity, biosensors for virus detection, micro-robots, and structures that can simulate living cells and provide a medium for their growth.
Kolmakov said: “We are introducing new tools (electron beams and X-rays running in liquids) into 3D printing of soft materials.” He and his colleagues passed a report published on ACS Nano on September 16, 2020. Their work is described in an article.
Link to this article:
Reprint Statement: If there are no special instructions, all articles on this site are original. Please indicate the source for reprinting:https://www.cncmachiningptj.com/,thanks!
 PTJ® provides a full range of Custom Precision cnc machining china services.ISO 9001:2015 &AS-9100 certified. Large scale machining Manufacturer of medical bags, providing 3D design, prototype and global delivery services. Also offering hard cases, semi-hard EVA, soft-sewn cases, pouches and more for OEMs. All cases are made custom according to specifications with infinite combinations of materials, molds, pockets, loops, zippers, handles, logos and accessories. Shockproof, water-resistant and eco-friendly options. Medical parts, emergency response, Electronic parts, corporate, education, military, security, sports, outdoors and construction industries. Services include case concept consultation, 3D design, prototyping,rototyping,CNC Drilling Services and manufacturing.Tell us a little about your project’s budget and expected delivery time. We will strategize with you to provide the most cost-effective services to help you reach your target,You are welcome to contact us directly ( [email protected] ) .
PTJ® provides a full range of Custom Precision cnc machining china services.ISO 9001:2015 &AS-9100 certified. Large scale machining Manufacturer of medical bags, providing 3D design, prototype and global delivery services. Also offering hard cases, semi-hard EVA, soft-sewn cases, pouches and more for OEMs. All cases are made custom according to specifications with infinite combinations of materials, molds, pockets, loops, zippers, handles, logos and accessories. Shockproof, water-resistant and eco-friendly options. Medical parts, emergency response, Electronic parts, corporate, education, military, security, sports, outdoors and construction industries. Services include case concept consultation, 3D design, prototyping,rototyping,CNC Drilling Services and manufacturing.Tell us a little about your project’s budget and expected delivery time. We will strategize with you to provide the most cost-effective services to help you reach your target,You are welcome to contact us directly ( [email protected] ) .
Link to this article:A 3D printing technology that can promote the manufacture of micro-medical devices inside the human body
Reprint Statement: If there are no special instructions, all articles on this site are original. Please indicate the source for reprinting:Tungusten,Thanks!^^








